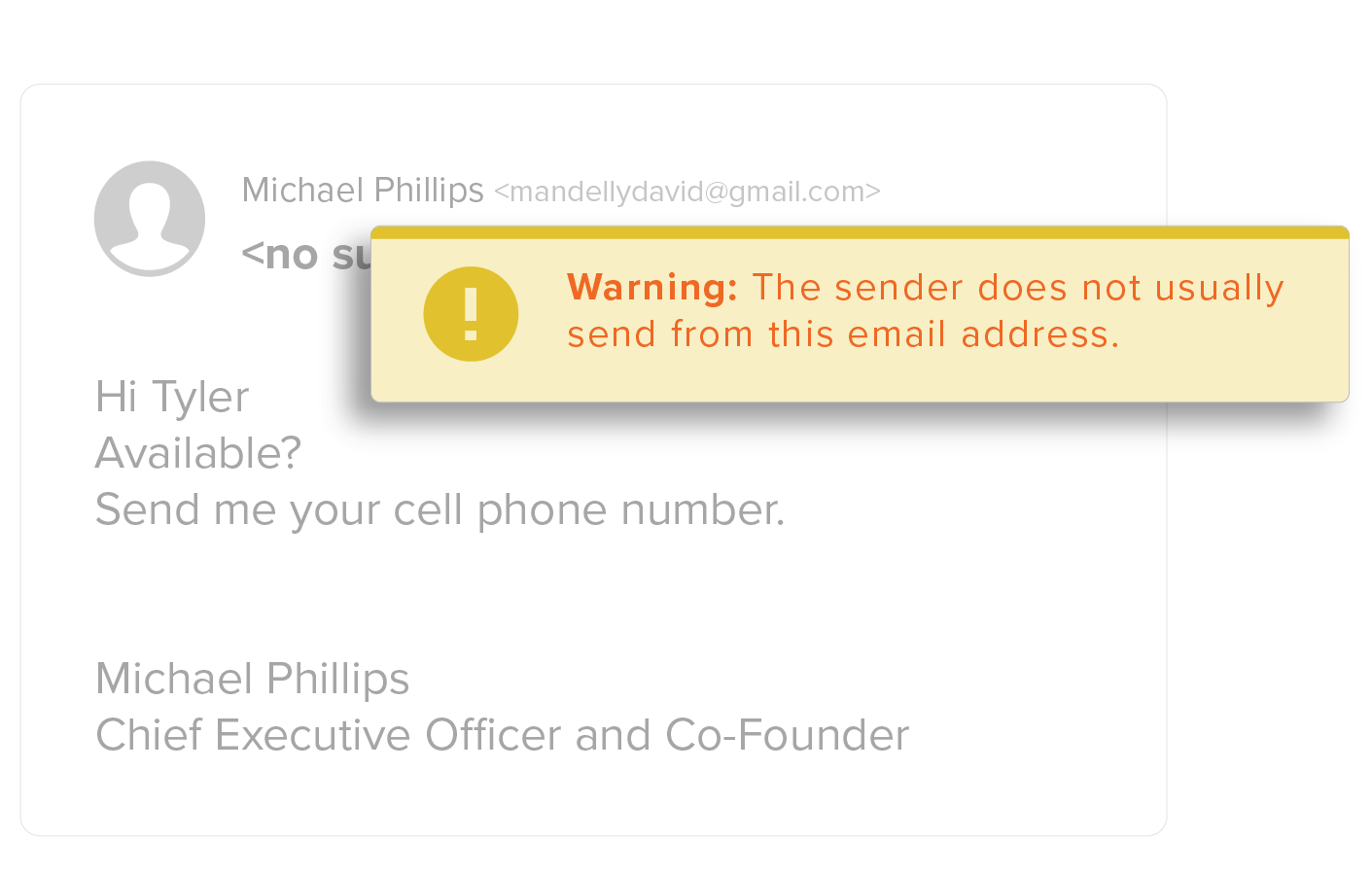
Detecting Executive Impersonation Attacks
Executive Impersonations
Business Email Compromise using Executive Impersonation attacks, are one of the most successful in a line of spear phishing attacks. Locating information about executives is easy, as most executive profiles are readily available to cybercriminals on corporate websites or social media sites like LinkedIn.
Cybercriminals know that employees respond to their executives quickly. And, because the phish appears to be from a trusted executive, users are tricked into taking action by transferring money or sharing sensitive information.
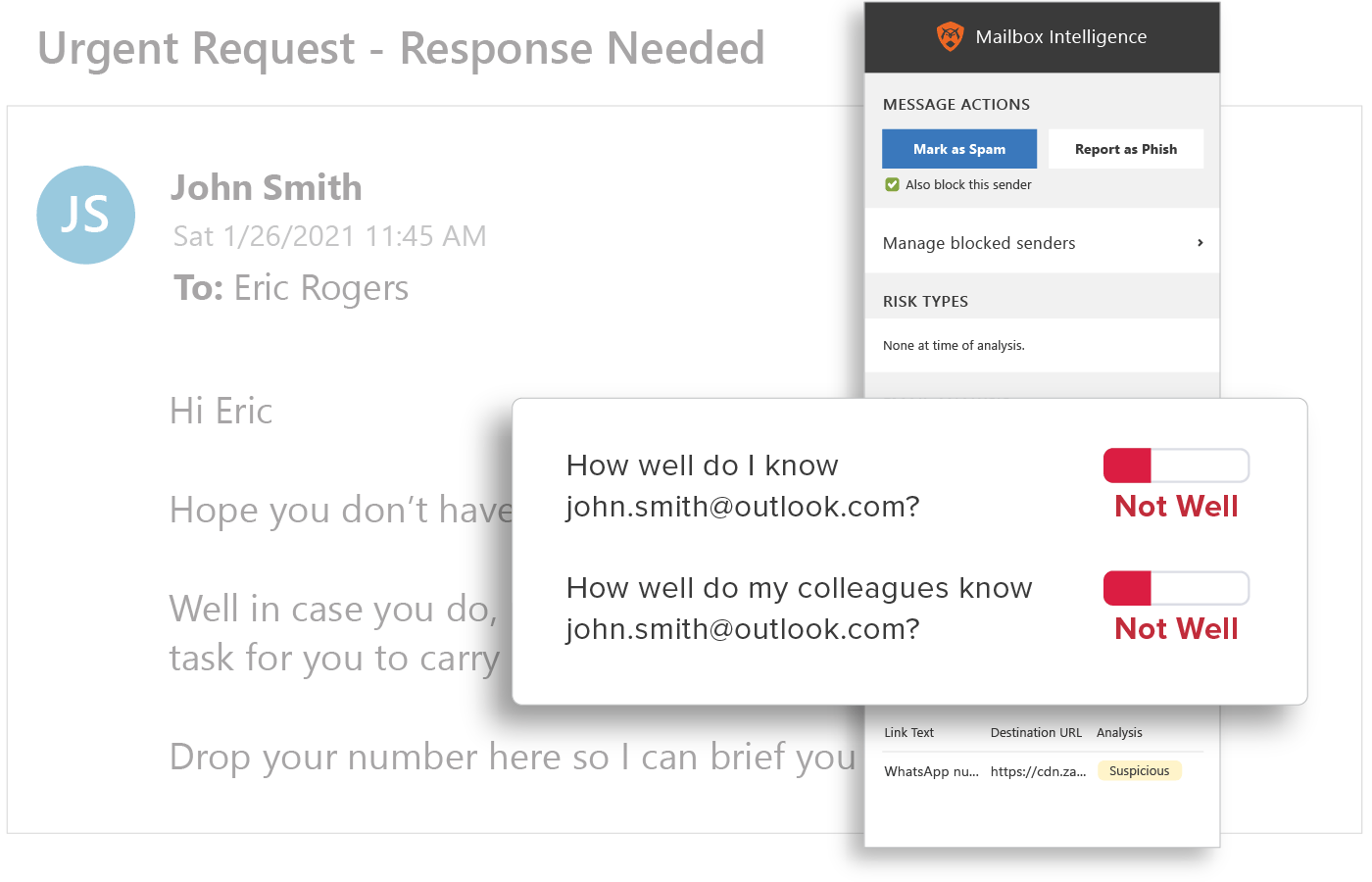
Behavioral Analytics
GreatHorn analyzes all communication patterns between senders and recipients using behavioral analytics within our AI and ML models, providing organizations with immediate detection and insight into email threats.
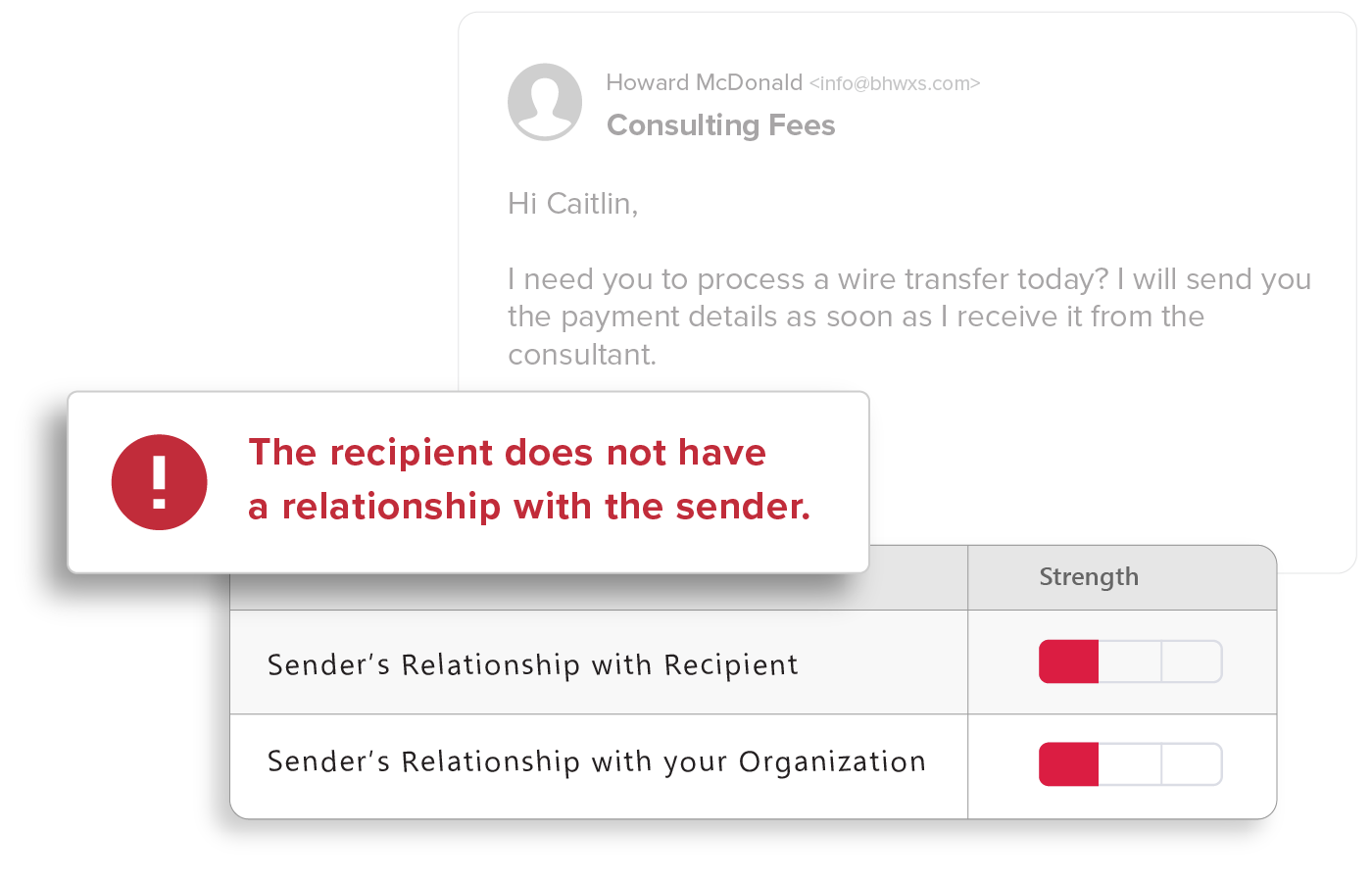
Relationship Strength
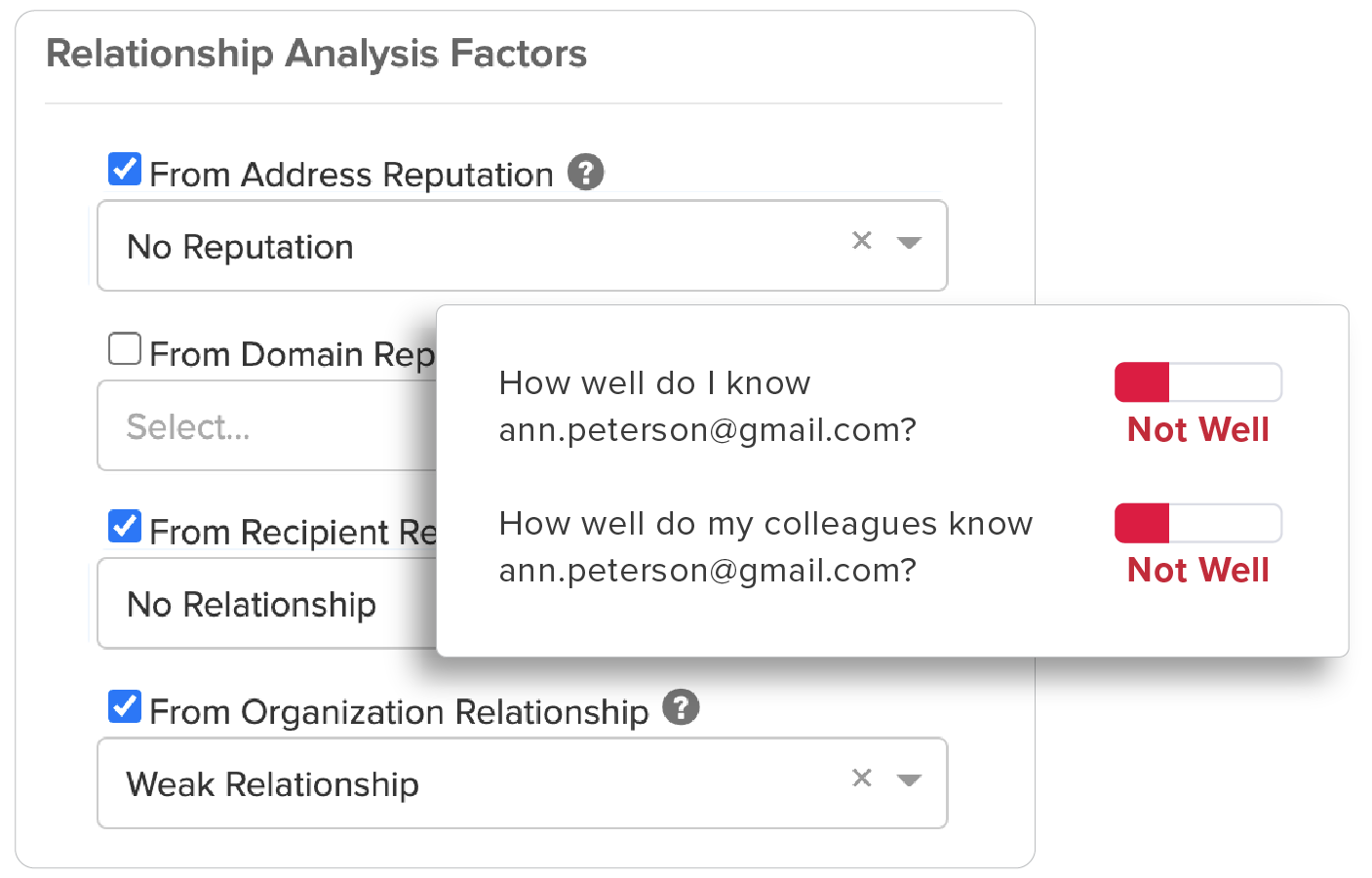
Strength of a sender’s individual relationship to the recipient, as well as a “friends of friends” system that accounts for the sender’s overall relationship with others in the recipient’s organization, provides sophisticated detection of BEC attacks.
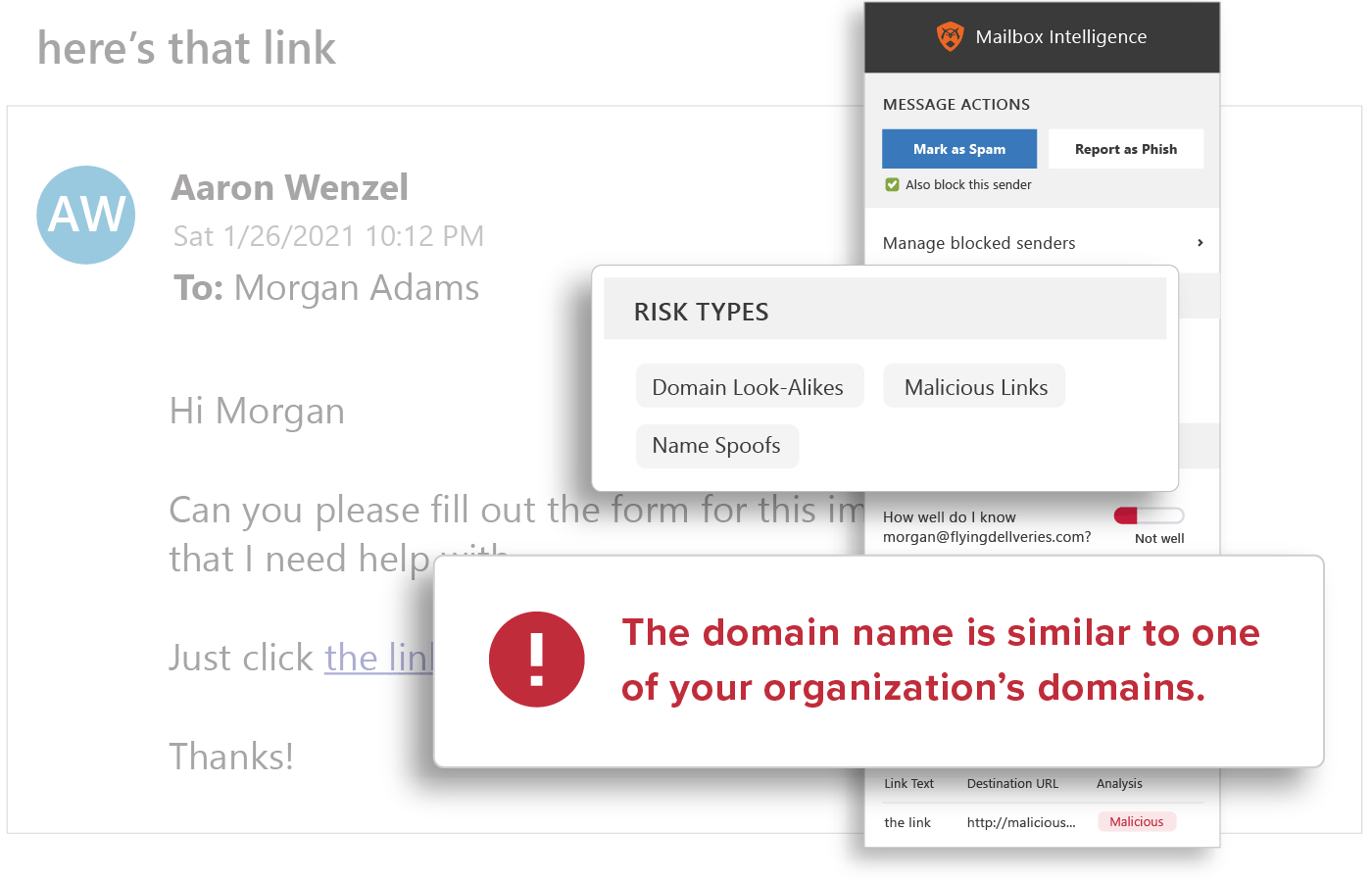
Spoofing Likelihood
GreatHorn’s email security engine analyzes permutations of organizations and employees to identify email threats including employee display name spoofs, domain spoofs, and domain look-alikes. GreatHorn identified Business Email Compromise (BEC) phishing emails by comparing against known email addresses, executive impersonation tactics, and email authentication standards.
Technical Fingerprints
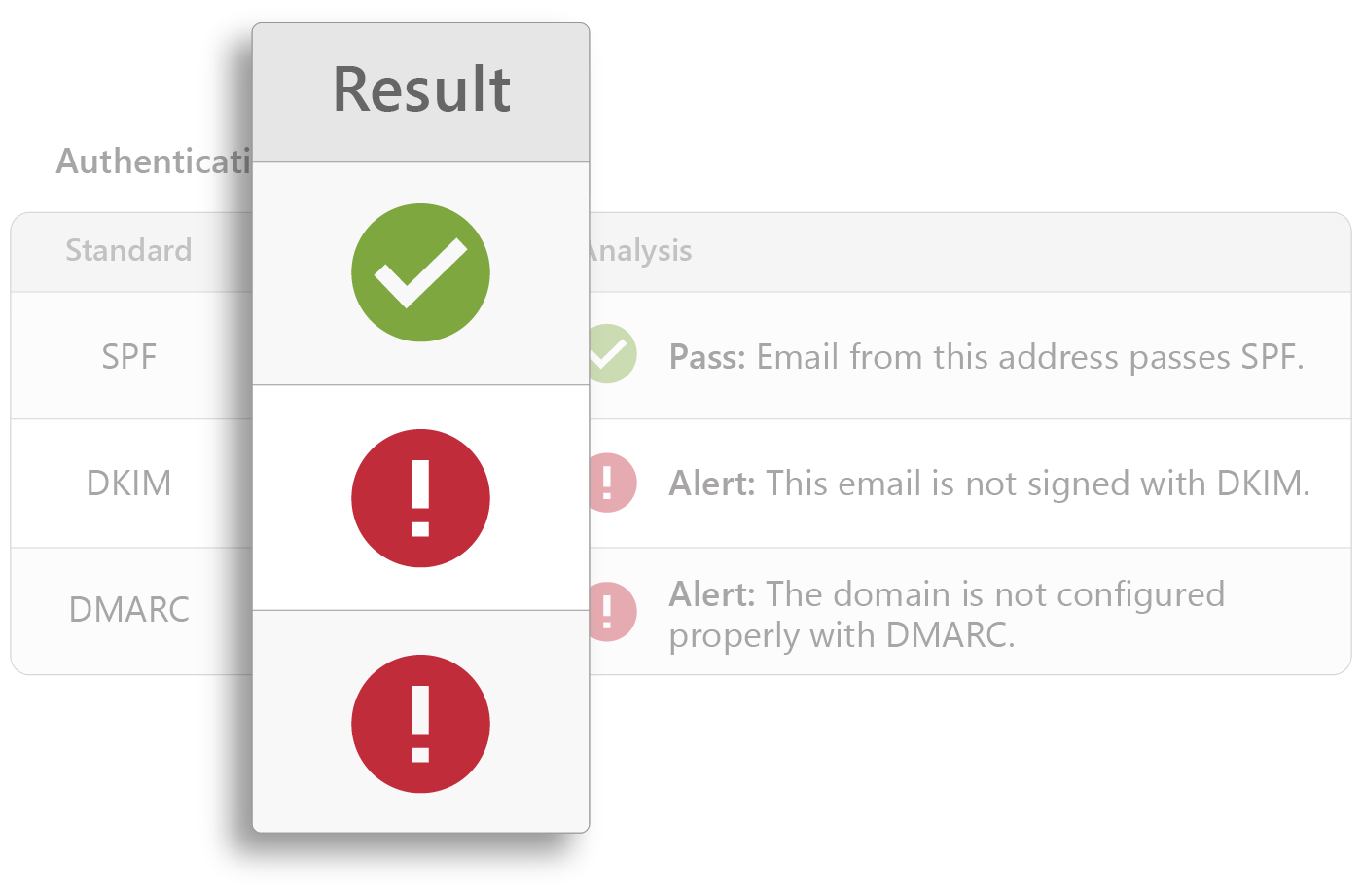
Sophisticated analysis of domain reputation, sending IP, and header information, including variations in expected authentication results for DMARC, DKIM, and SPF, detects email threats instantly.
Content Analysis
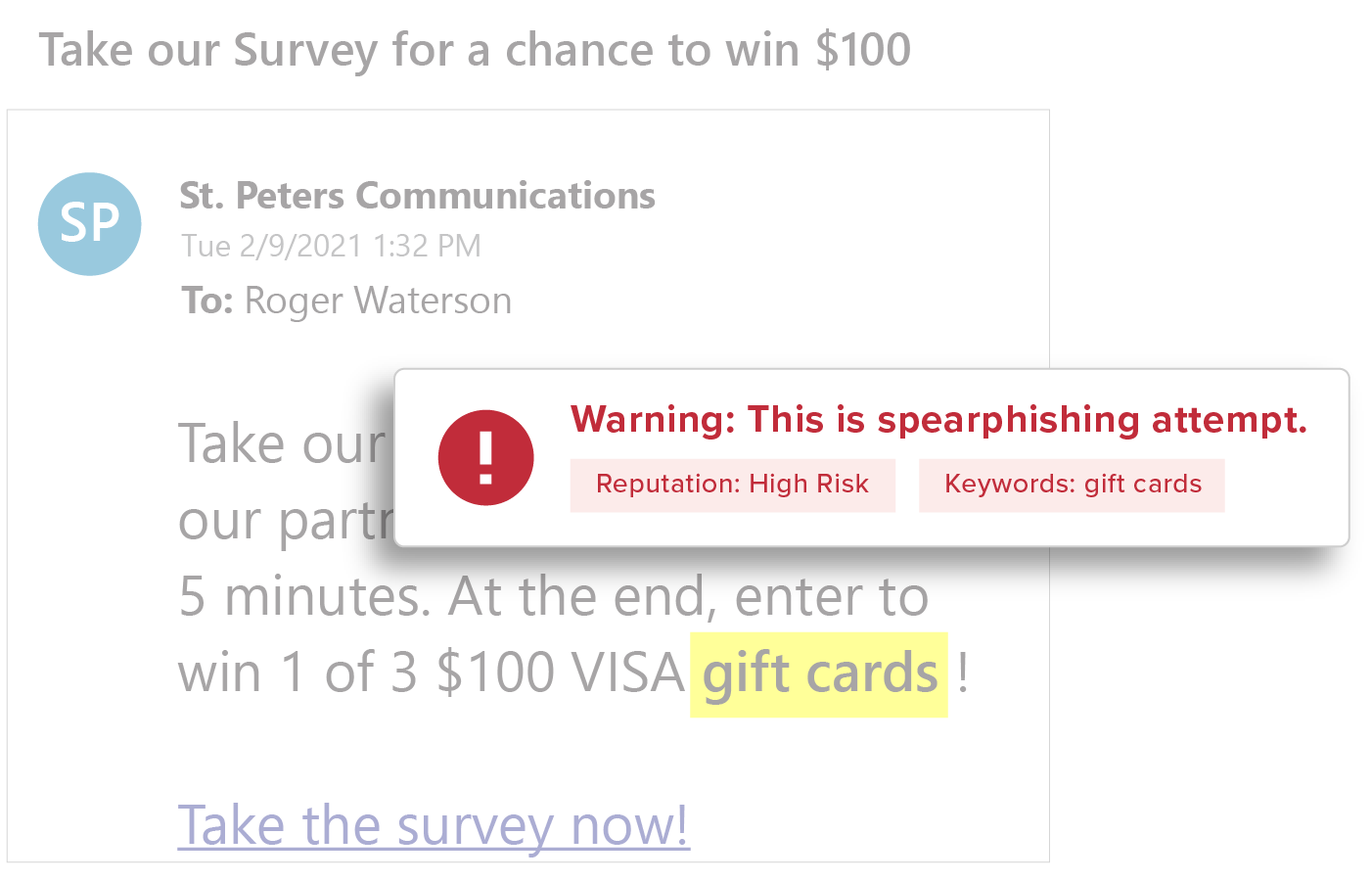
Deep content inspection based on keywords, regular expressions (RegEx), attachments, and URLs, to identify common spear phishing tactics—wire transfer and W2 requests, credential theft attacks, business service impersonations—all without storing the content or the mail.
Communication Patterns
GreatHorn’s ML engine establishes an understanding of communication patterns unique to a specific individual and a specific organization, such as email frequency, volume, recipients, sending patterns and more.
![[eBook] Things to Consider: Microsoft 365 + GreatHorn](https://www.greathorn.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/eBook-Microsoft-365-GreatHorn.png)
![[eBook] Things to Consider: Google Workspace + GreatHorn](https://www.greathorn.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/eBook-Google-WorkspaceGreatHorn.png)
![[Whitepaper] Measuring the Value of Email Security Solutions](https://www.greathorn.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Whitepaper-Measuring-the-Value-of-Email-Security-Solutions.png)
![[Report] 2023 State of Email Security: Key Trends and Insights](https://www.greathorn.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Report-2023-State-of-Email-Security.png)