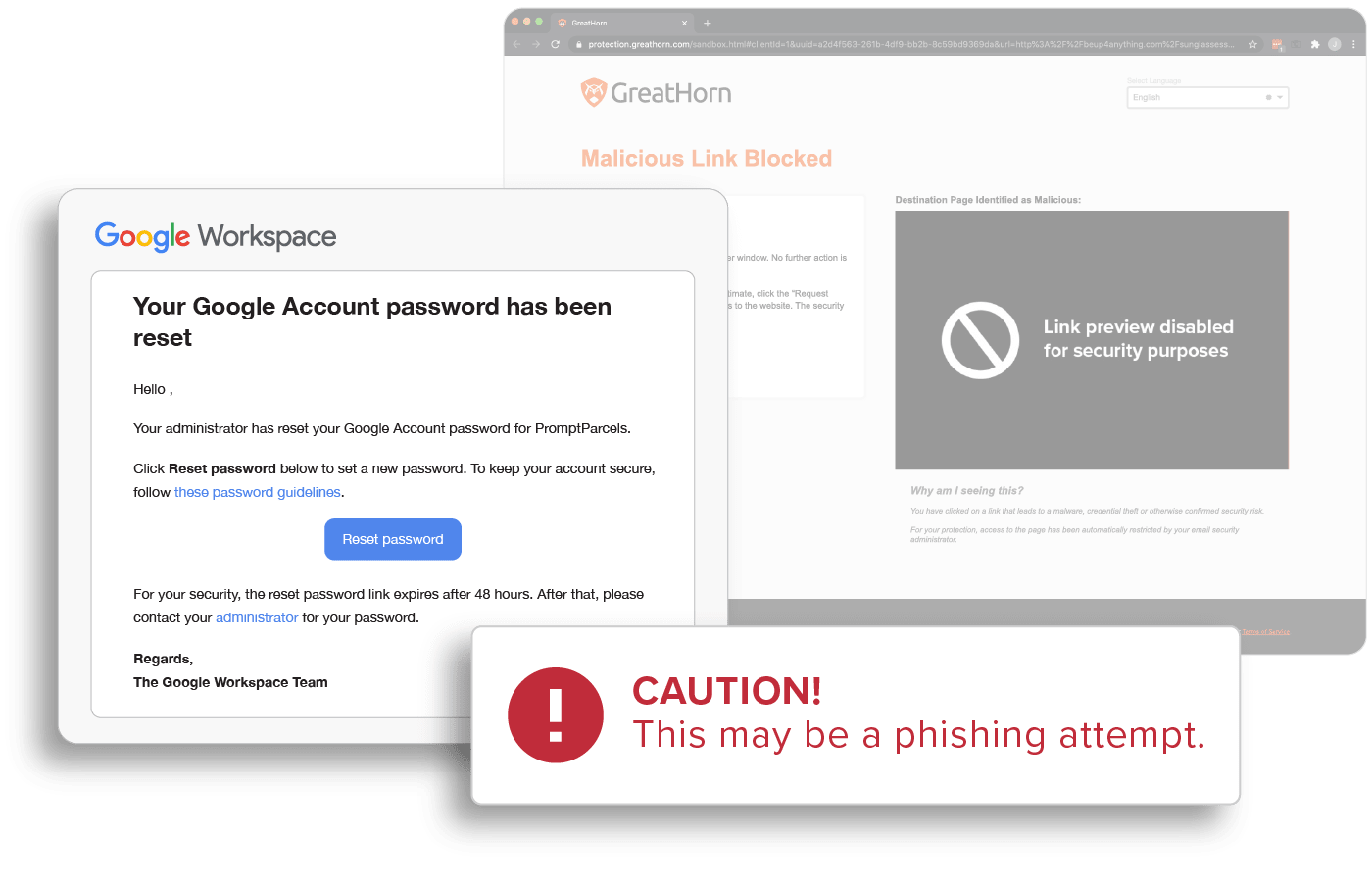
Detecting Credential Theft Attacks
Credential Theft
Attackers leverage a wide variety of techniques to perform credential harvesting attacks or email account compromise, to steal credentials or capture other personal information, often from fake login pages. The ability to impersonate business applications and relationships makes users a target for credential theft and email account compromise.
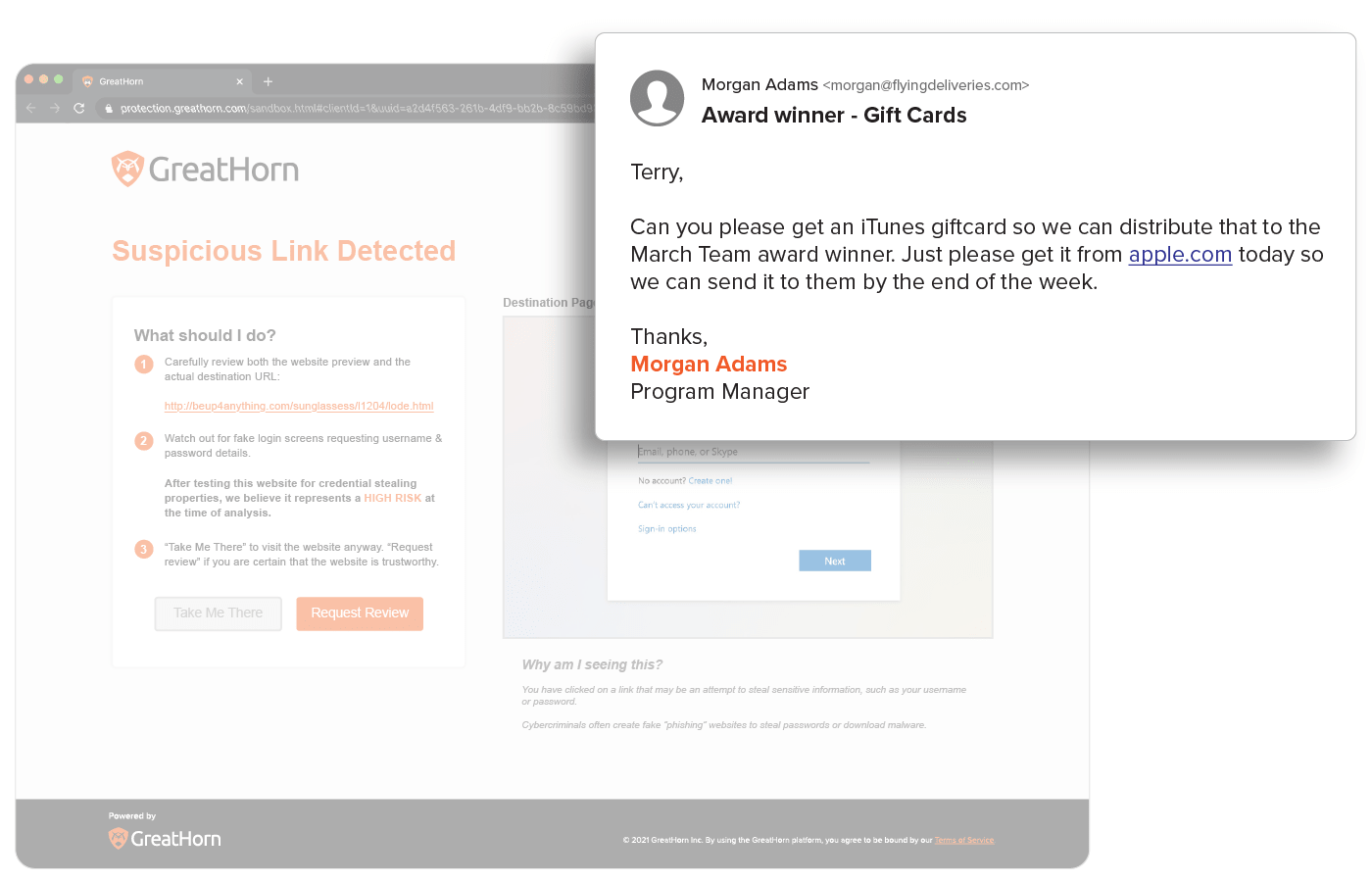
Suspicious and Malicious URL Detection
URLs are easy to manipulate so that no two are delivered the same and are a top threat vector within spear phishing attacks. With GreatHorn, all URLs are inspected upon delivery to identify and detect malicious websites, but also detects suspicious URLs that turn malicious, using time-of-click analysis and computer vision.
Behavioral Analytics
GreatHorn analyzes all communication patterns between senders and recipients using behavioral analytics within our AI and ML models, providing organizations with immediate detection and insight into anomalous emails.
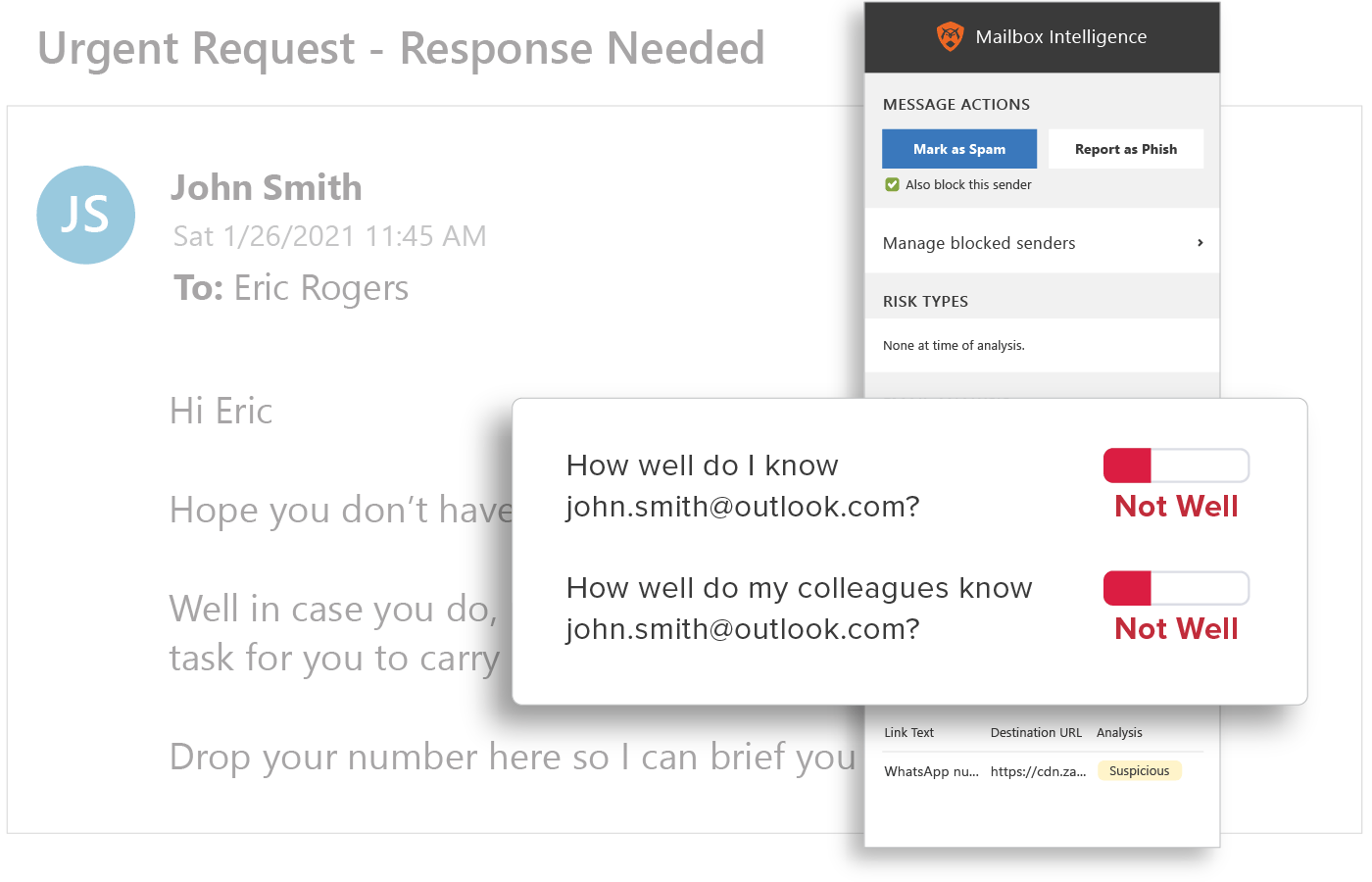
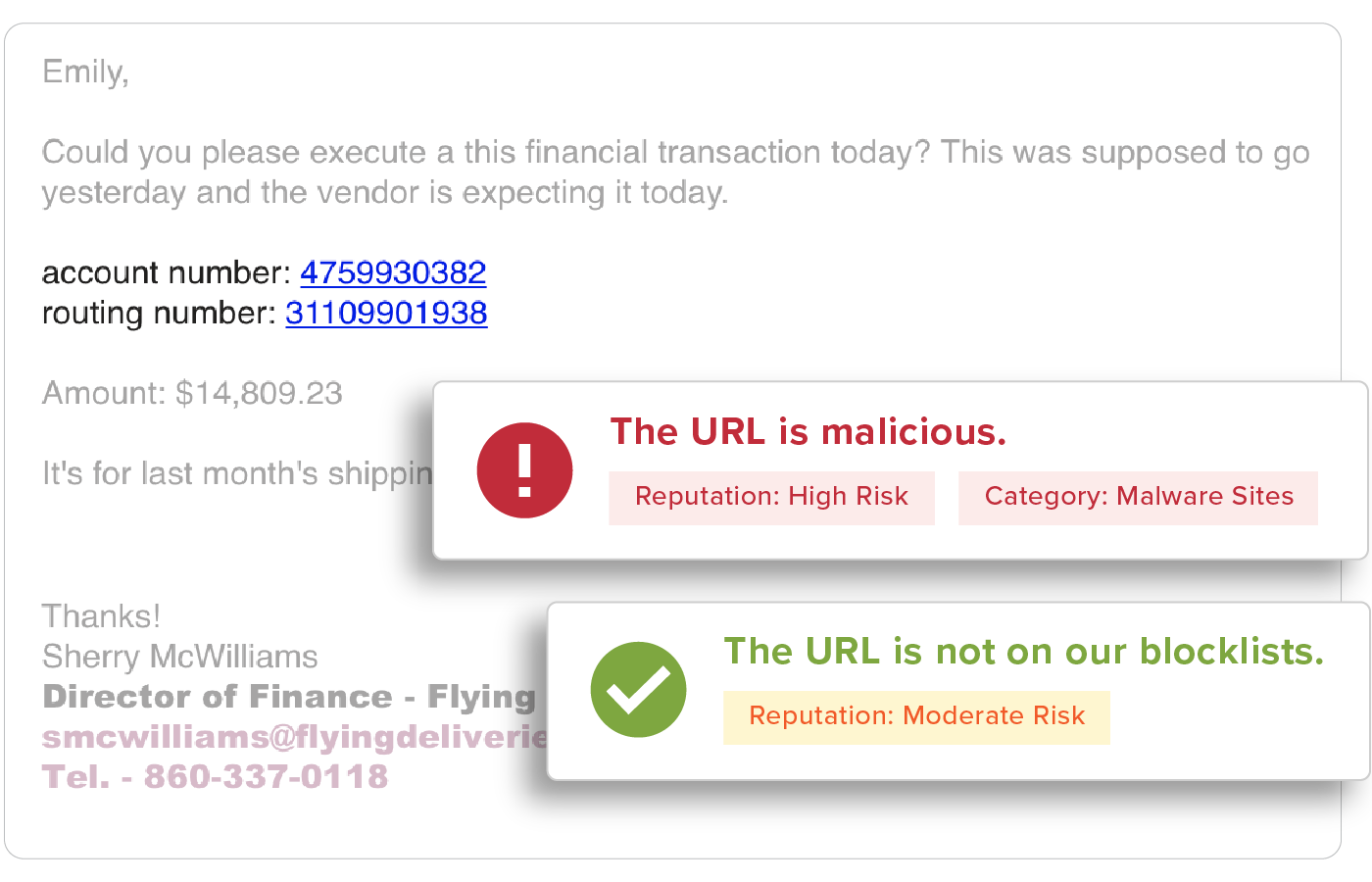
End User Education
Provide users with the context they need to help them make better decisions by applying automated and customized smart banners, Mailbox Intelligence, Suspicious Link pages, and more, to prevent users from having their corporate credentials stolen.
How do credentials become compromised?
Information and data between individuals and organizations is most often worked on through online collaboration platforms (i.e. Microsoft SharePoint, Google Docs, DocuSign, etc). Instead of sending this information as an attachment, data is shared through email using links to documents. And, when accessing this information, users must first use their corporate credentials to authenticate and login to the platform.
Threat actors use phishing emails, impersonating legitimate collaboration platforms with links to credential harvesting webpages, stealing credentials. Once the threat actor has gained access to corporate credentials, they can take the compromised passwords to steal personal information and corporate information, resulting in data breaches.
How do I know if my account is compromised?
Many organizations do not have the security systems in place to identify if an account was compromised. However, multi factor authentication (MFA) is one of the protocols most commonly used to protect against stolen credentials and the subsequent access to corporate information. MFA requires more than one method of authentication in order to verify a user’s identity. For more information on MFA, click here.
Biometric authentication is a more secure way of identifying compromised accounts. By using biometric authentication, an organization can capture an employee’s unique typing pattern to verify an employee’s identity, including keystroke speed, pressure, and timing, to reduce exposure from any compromised accounts, prevent emails from being sent, and notify administrators of compromised passwords. For more information on how to protect again account takeovers, click here.
What percentage of cyber incidents are a result of compromised credentials?
Compromised credentials are the top vector by which threat actors gains access to an organization, resulting in 61 percent of all breaches*. With the ability of threat actors to identify high value targets (HVTs), with privileged access to systems and networks, combined with the use of spear phishing to steal corporate credentials, organizations can easily become of victim of a data breach.
![[eBook] Things to Consider: Microsoft 365 + GreatHorn](https://www.greathorn.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/eBook-Microsoft-365-GreatHorn.png)
![[eBook] Things to Consider: Google Workspace + GreatHorn](https://www.greathorn.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/eBook-Google-WorkspaceGreatHorn.png)
![[Whitepaper] Measuring the Value of Email Security Solutions](https://www.greathorn.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Whitepaper-Measuring-the-Value-of-Email-Security-Solutions.png)
![[Report] 2023 State of Email Security: Key Trends and Insights](https://www.greathorn.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Report-2023-State-of-Email-Security.png)